

Just to refresh your memory: We are always talking about IRON and the thousands of combinations that make it the most versatile metal used by humans, as well as the most abundant on our planet.
If we add a pinch of carbon (0.03% to 2%) to IRON, it becomes STEEL, significantly increasing its mechanical strength, among other characteristics.
Carbon is also a very abundant element in nature, which facilitates steel production and local supply anywhere in the world. Another advantage of steel is that it can be recycled indefinitely with almost no loss of its properties.

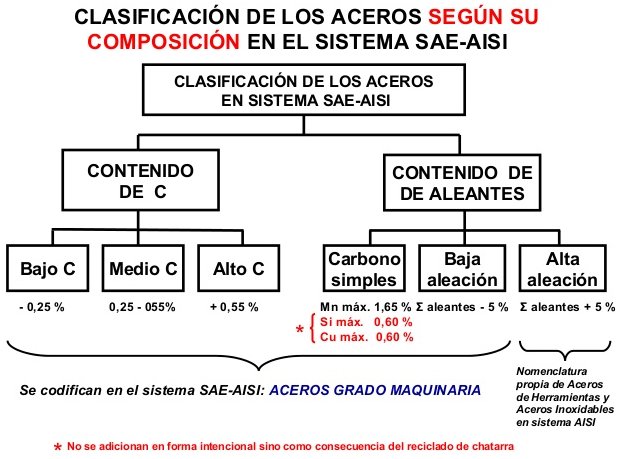
ALLOY STEEL is steel that incorporates one or more chemical elements, in addition to carbon, in various proportions ranging from 1% to 50% to improve its mechanical or thermodynamic properties, such as impact resistance, elasticity, expansion, fatigue resistance, etc.
These are divided into two categories: low-alloy steels and high-alloy steels, depending on the amount of added elements. The boundary between these categories is not very clear and is around 6% of the mass. Below 6%, they are usually considered low-alloy steels, and above that, high-alloy steels.
Typically, the term alloy steel refers to low-alloy steels, while high-alloy steels are known as special steels and are given more specific names for each variant.
The most commonly used elements in alloys are nickel, manganese, chromium, vanadium, molybdenum, silicon, lead, selenium, and boron. Less frequently, aluminum, titanium, cobalt, copper, cerium, niobium, zirconium, and tungsten are used.

The variety of possible alloys is almost infinite, as is the diversity of characteristics that steel acquires depending on the proportion of alloying elements. Alloy steel can be endowed with attributes impossible to achieve with its ordinary carbon steel version. Some of the improvements that can be obtained are:
Aluminum: Helps deoxidize molten steel and produces a finer grain of better quality.
Boron: Improves hardenability.
Chromium: Increases hardening depth and improves wear and corrosion resistance.
Copper: Improves corrosion resistance.
Manganese: In amounts greater than 1%, it facilitates rolling and hot molding. It also improves tempering and increases strength and hardness.
Molybdenum: Improves hardness and toughness. Facilitates tempering in oil or air.
Nickel: Reduces hardening temperature, facilitating hot molding. Also minimizes deformation during tempering. Improves strength without sacrificing ductility.
Silicon: Mainly used as a deoxidizing and stabilizing complement to facilitate alloying with other elements.
Titanium: Acts as a deoxidizer and increases resistance to high temperatures.
Tungsten: Provides hardness at very high temperatures.
Vanadium: Ideal for tools, improves hardness, impact resistance, and reduces fatigue.
The AISI nomenclature consists of 4 digits to organize the different types of steel. The first two digits indicate the main alloy, and the last two refer to the amount of carbon. In some cases, there are 5-digit numbers, where the last three refer to the percentage of carbon. Occasionally, letters are added for special cases.
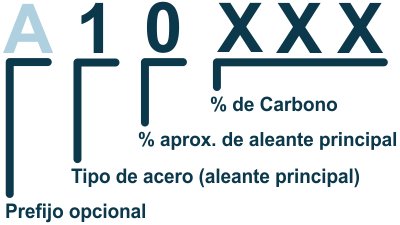
The following list shows which element each number in the first position of the nomenclature represents.
For example: If the first digit is a 2, it is nickel steel, such as AISI 23XX, which contains 3.5% nickel. If the first digit is a 3, it is Nickel-Chromium steel, for example, AISI 31XX has 1.25% nickel and 0.65% chromium.
23XX: Connecting rod bolts, pins, etc.
25XX: Gears, cams, and crankshafts.
51XX: Engine bolts, springs, etc.
52XX: Bearings, crushing machinery.
Widely used in stainless steels and heavy-duty applications.
31XX: Manganese steels. Used where high wear resistance, general strength, and ductility are required, such as in excavator teeth, grinding and crushing machines, shafts, gun barrels, and railroad rails.
40XX and 44XX: Gears and less severe applications. With higher carbon content, they are excellent for suspension springs.
41XX: Known as chromium-molybdenum steels. Used for ultralight aircraft and bicycle frames as an alternative to aluminum, although heavier. The 4140 is excellent for crankshafts, driveshafts, connecting rods, bolts, gears, etc.
Surface treatment for crankshafts and tools. Excellent hardness and wear resistance. A great option for knives.
With 1 to 2% silicon, it is used for structural and naval applications. Hadfield silicon steel (0.01% C and 3% Si) is used in electrical machinery.
9260: Springs, punches, and chisels.
We hope you found this article useful. If you want to learn more, you might be interested in the article about STAINLESS STEEL.





They are already part of the Job Board



